The Goffstown giant pumpkin weigh-off and regatta is back
By Katelyn Sahagian
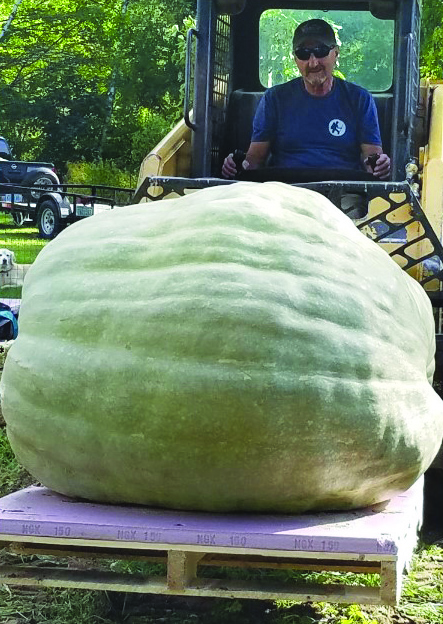
Giant pumpkins will take over the Piscataquog River in Goffstown on Sunday, Oct. 16. The day before, the pumpkins will be weighed, hollowed out and decorated for the race.
The event, which started as a way for local giant pumpkin growers to see who had the best crops, has become a national — and international — phenomenon.
“We were contacted by a television company in Japan to see if they can get involved somehow,” said Tina Lawton, president of Goffstown Main Street Program. “It’s known far outside New Hampshire. People come from all over to come and see it.”
Back in 2000, when James Beauchemin started the pumpkin weigh-off, he said that there was nowhere in New Hampshire for giant pumpkin growers to show off the squashes they had spent weeks growing and caring for. He and a few of his friends created the New Hampshire Giant Pumpkin Growers Association and decided that they could hold their own showcase.
Beauchemin wanted something special to happen with the pumpkins after they had been weighed. He said he had heard of a group in Canada that did a pumpkin boat race, where growers hollowed out their giant pumpkins and used kayak paddles to see who could get to the finish the quickest.
“There was one giant pumpkin club in Nova Scotia that did pumpkin races. … They may even still do it,” Beauchemin said. “But I brought it to America.”
The biggest difference between the boat race in New Hampshire and the one in Canada is that Goffstown’s regatta has motors fitted to the boats, giving the pumpkin vessels a little more speed and the captains a greater chance for competition.
While the growers were the first to compete in the makeshift boats, the regatta has become less something for regular people to race in, and more something for public figures in Goffstown and southern New Hampshire in general, Lawton said.
In addition to a few popular teachers racing the boats, WMUR anchor Erin Fehlau will be captaining one of the boats. In the past, Hippo has even sponsored a boat.
While the regatta is the star of the show, Lawton said, there are other events that people can check out throughout the weekend.
Saturday will be the day that all the pumpkins are weighed and, when that’s ended, they’ll be moved closer to the river, Lawton said. The captains will begin the process of hollowing out and decorating their boats in line with this year’s theme, “There’s no place like home.”
“The theme for this year’s decoration is Wizard of Oz,” Beauchemin said. “I was told someone is going to build a tiny house on top of a pumpkin with legs of the Wicked Witch of the East sticking out.”
Sunday will start with a 10K race, and right before the regatta there will be the ever-popular pumpkin drop. Beauchemin said the pumpkin this year will be more than 2,000 pounds, and it’ll be dropped from approximately 75 feet.
In addition to the pumpkin-related events, there will be a slew of local vendors selling handmade crafts, different food options to choose from, a dog costume contest, an art show, a pie eating contest and live entertainment.
Every year, the event seems to grow in popularity, said Lawton.
“We get emails and calls from people all over the states asking when it’ll be,” Lawton said. “Lots of residents have families schedule their visits around this event.”
Goffstown Pumpkin Weigh-off and Regatta
Where: Main Street, Goffstown
When: Saturday, Oct. 15, starting at 9 a.m.; Sunday, Oct. 16, starting at 8 a.m., Regatta begins at 3 p.m.
Price: Free
Visit: goffstownmainstreet.org/regatta
Featured photo: Courtesy photo.